Testosterone is the male sex hormone that’s best known for promoting masculine characteristics. Testosterone is also the main hormone that controls libido in both men and women. If testosterone levels fall for any reason, low sex drive will result. For men, low testosterone levels are also associated with long-term health risks including an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Like other steroid hormones, testosterone is produced in the body from cholesterol, which is first converted into the hormone, pregnenolone. From there, pregnenolone is converted into other hormones such as DHEA, progesterone, and oestrogens. Pregnenolone and DHEA are available as supplements in some countries, but if you think you have testosterone deficiency syndrome it’s best to take these under medical supervision.
Testosterone in men
Healthy men produce between 4mg and 10mg testosterone per day, of which 95% is made in the testicles and a small amount (5%) is produced in the adrenal glands. The highest testosterone levels occur during the teens and early twenties, and gradually reduce in later life. Testosterone levels also vary with the time of day, and is highest in the morning, then falls by around a third as the day progresses, although this diurnal variation is not typically seen in men over 50 years of age.
In males, testosterone hormone is responsible for:
- Maintaining general strength, energy levels and stamina
- Maintenance of sex drive
- Growth of the larynx and deepening of the voice
- Growth of the penis, testes, prostate gland and scrotum at puberty
- Maintenance of male patterns of hair growth
- Increasing muscle bulk and regulating fat deposition
- Secretion of fluids from the prostate gland
- Stimulation of sperm production
- Maintenance of erectile function
Testosterone may also play a role in the attractiveness of male odours to women.
Testosterone deficiency
Male testosterone levels naturally fall after middle age by as much as 1% a year beginning around the age of 40.
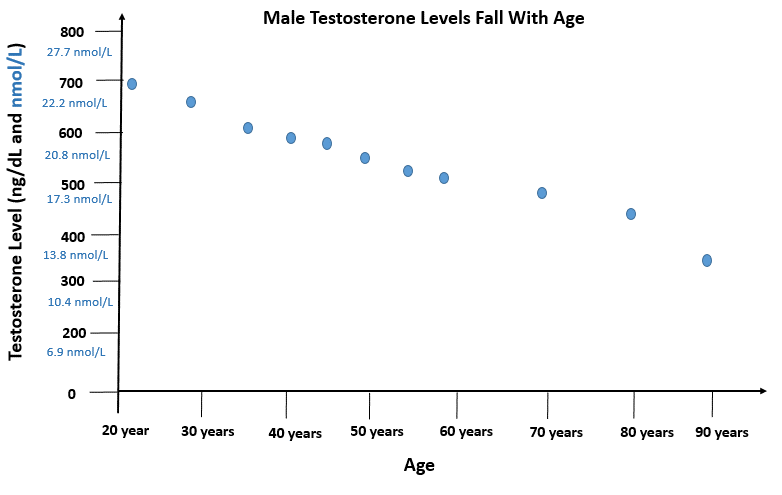
Overall, an estimated 1 in 12 men in their 40s to 60s have a testosterone level below the normal range – a condition known as testosterone deficiency syndrome (TDS).
Some researchers have found the chance of having testosterone deficiency (or androgen insufficiency) increases with age so that as many as 1 in 5 men (20%) over 60, and 1 in 3 men (35%) over the age of 80 are affected. Other studies have found lower rates of testosterone deficiency, however, and estimates vary widely.
The European Male Aging Study which involved over 3,000 men aged 40 to 79 years found that only around 1 in 50 of these men (2.1%) had definite testosterone deficiency and that 75% maintained normal testosterone levels into old age. However, almost 1 in 8 men (11.8%) had secondary testosterone deficiency due to lower levels of pituitary hormones (LH and FSH) which normally stimulate the testes to produce testosterone. Most of these men did not have symptoms and were deemed ‘worthy of observation but not treatment with testosterone’. This could be a shame as low testosterone levels increase the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and osteoporosis.
Symptoms of male testosterone deficiency
The symptoms associated with falling testosterone levels have been referred to as the male menopause (andropause or viripause).
Testosterone deficiency can lead to symptoms of tiredness, irritability, reduced sex drive and a decrease in sexual performance. You may lose muscle mass and strength, gain weight and experience sleep disturbances and fatigue. Changes in fat distribution can lead to an expanding waist (the so-called beer belly) and enlargement of the male breasts (gynecomastia, sometimes referred to as moobs). Some men also experience excessive sweating, hot flushes, reduced concentration, poor memory, and mood swings with anger, irritability, sadness or depression.
The ADAM Questionnaire for testosterone deficiency
If you’re male and aged 40 or over, you can find out if you could have low testosterone levels by completing the ADAM (which stands for Androgen Deficiency in Aging Males) questionnaire, developed by Dr John Morley, an endocrinologist at Saint Louis University, Missouri.
The ADAM questionnaire consists of ten simple questions, as follows:
| 1 | Do you have a decreased libido (sex drive)? |
| 2 | Do you have a lack of energy? |
| 3 | Do you have a decrease in strength and/or endurance? |
| 4 | Have you lost height? |
| 5 | Have you noticed a decreased ‘enjoyment of life? |
| 6 | Are you sad and/or grumpy? |
| 7 | Are your erections less strong? |
| 8 | Have you noticed a recent deterioration in your ability to pay sports? |
| 9 | Are you falling asleep after dinner? |
| 10 | Has there been a recent deterioration in your work performance? |
If you answer YES to questions 1 or 7, or to any 3 other questions, you may have testosterone deficiency syndrome. Although the ADAM questionnaire cannot diagnose whether or not you have testosterone deficiency, research suggests it is a sensitive screening questionnaire for androgen deficiency and can help alert men to a potentially serious health condition that needs review and possibly treatment. If you think you could have testosterone deficiency, your doctor can request a blood test to measure your testosterone levels.
Testosterone replacement therapy
Male hormone replacement therapy with testosterone is available on prescription to treat testosterone deficiency. Treatment aims to raise testosterone levels to normal, not to excessively high levels.
Guidelines usually recommend treatment with testosterone replacement if your testosterone level is lower than 8 nmol/L (230 ng/dL), based on two separate measurements taken in the morning (between 8am and 11 am) when your testosterone levels are usually at their highest.
A testosterone level higher than 12 nmol/L (346 ng/dL) does not usually require testosterone treatment. If your level is borderline (between 8 nmol/L and 12 nmol/L) you might need testosterone therapy if you have symptoms.
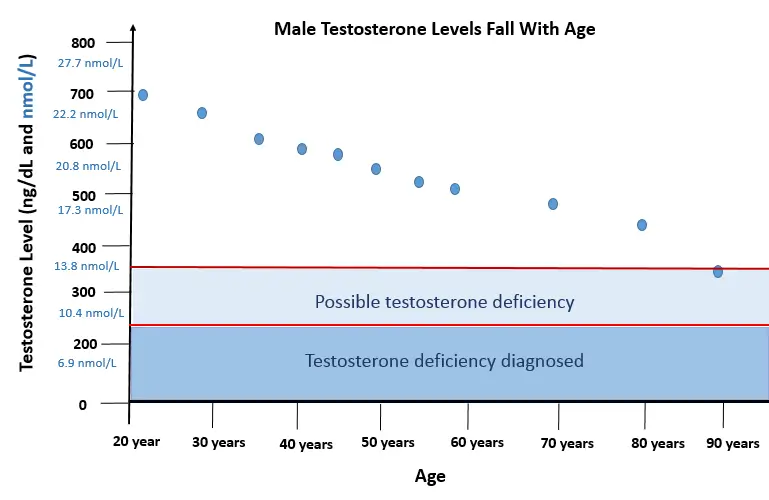
As treatment is usually required for at least 6 months (when borderline) and is often needed lifelong, testosterone replacement therapy is only started after your doctor is satisfied that you have an established hormone deficiency.
However, as the above graph shows, your testosterone levels have to be significantly low to warrant medical treatment. A man aged 40 or over could have a testosterone level that is almost half that in his youth, but still be considered within the normal range.
Sometimes symptoms associated with testosterone deficiency, such as loss of energy and low sex drive can occur despite having a normal testosterone levels, and may be due to reduced interaction between circulating testosterone and its receptors (which becomes more common with age), or to more testosterone becoming bound to protein (and therefore less active) in the circulation. Some doctors may be prepared to prescribe a trial of testosterone replacement to see if this improves symptoms.
If you do not warrant medical treatment, are natural testosterone supplements likely to help?
Best testosterone supplements
A range of supplements that claim to boost testosterone levels naturally are available online. These supplements claim to help:
- build muscle mass and strength
- reduce excess body fat
- improve concentration and focus
- reduce tiredness and fatigue
- improve low libido.
As a doctor used to prescribing hormones and other medical treatments, I was naturally sceptical of claims that a natural supplement could enhance testosterone production, and spent several hours investigating the ingredients found in a variety of male supplements and have concluded that one of the best testosterone supplements is Testogen. Here’s why.
Testogen Review
Testogen provides (per serving of 4 capsules):
I was surprised to find there is good evidence that the ingredients included in Testogen can actually boost testosterone production, which explains why the brand has a Medical Advisory Board of four consultants that includes Alfred Hasselbacher, a renowned Professor of Medicine.
Magnesium is important for testosterone production, especially in older men. A study involving 399 Italian males found that magnesium levels were strongly associated with total testosterone levels, even after adjusting for weight (body mass index) and DHEA-s hormone levels.
Zinc is one of the most important minerals for healthy testosterone levels, sex drive, prostate health and male fertility. Low zinc levels can even suppress testosterone levels enough to delay puberty in adolescents. When zinc levels were assessed in 88 men, those with normal testosterone levels had a significantly higher zinc level than those with low testosterone levels.
Boron is a trace element who role in health is not fully understood. It does, however, appear to be important for testosterone production. In one study, eight males took 10 mg boron every day, with breakfast, for one week. Blood tests showed that, within six hours of taking a dose, they had a significant decrease on sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) which binds to testosterone so it becomes less active. As a result, their levels of free, active testosterone increased and, interestingly, their blood levels of oestrogen (estradiol) fell significantly. This was the first human study (carried out in 2011) to show that boron has a rapid effect on increasing levels of free testosterone.
Vitamin B6 has been shown in preclinical studies to increase the ability of cells to respond to testosterone hormone. Vitamin B6 is believed to increase the action of testosterone (and other steroid hormones) by recycling steroid receptors from the cell nucleus back into the cell.
Vitamin D3 is now known to have beneficial effects on the male reproductive tract. A study involving 54 healthy men assess the effects of taking either 83mcg (3,332 IU) vitamin D supplements per day for 1 year against placebo. There was a significant increase in total testosterone, bioactive testosterone and free testosterone levels in those taking vitamin D but no significant change in any testosterone measure in the men taking placebo. Other studies have confirmed these effects, but some have not. Vitamin D may only have a significant effect if you are vitamin D deficient.
Vitamin K1 supplements have been shown in preclinical studies to significantly increase testosterone levels in rats, and is believed to be involved in the conversion of cholesterol to testosterone in the testes. Supplements were found to enhance testosterone production in elder rats.
Nettle extracts contain high concentrations of hormone-like substances such as beta-sitosterol. They are widely used to improve male urinary symptoms due to an enlarged prostate gland. Nettle extracts appear to work by competing with testosterone to bind with sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) in the circulation. As a result, more testosterone remains free and active within the circulation.
D-aspartic acid is an amino acid involved in the synthesis of luteinising hormone which is made in the pituitary gland and travels to the testes to kick-start testosterone production. A study involving 43 healthy men compared the effects of taking d-aspartate supplements (3.12g) at breakfast for 12 days against placebo. Supplements were found to enhance production of pituitary luteinising hormone (which stimulate testosterone production in the testes) and release of testosterone hormone.
Fenugreek is an Ayurvedic herbal medicine used to enhance testosterone levels and male fertility. Research shows that fenugreek seed extracts can improve androgen deficiency and sexual function. A group of 120 healthy aging males aged between 43 and 70 years were given either 600mg fenugreek seed extract at day, or placebo, for 12 weeks. Fenugreek significantly improved quality of life, sexual function, the number of morning erections and frequency of sexual activity compared with placebo. Blood levels of total testosterone and free, active testosterone also increased compared to placebo. The researchers concluded that fenugreek seed extract is a safe and effective treatment for reducing symptoms of androgen deficiency and increasing serum testosterone in healthy middle-aged and older men. These findings have been confirmed in other studies, with free testosterone levels improving by up to 46%, as well as increasing sperm counts and sperm quality.
Red ginseng is one of the oldest known herbal medicines used to improve sex drive and sexual performance in males. Ginseng has a Viagra like action, increasing levels of nitric oxide (NO) a substance which dilates blood vessels and is essential for normal erectile function and sexual arousal.
At least 7 trials involving 349 men found that red ginseng is almost two and a half times better than placebo in improving erectile function in studies lasting from 4 to 12 weeks. One of the latest studies investigate the effect of red ginseng on hormone levels in 62 men with metabolic syndrome. Compared with placebo, those taking ginseng showed significant improvements, within 4 weeks, on mitochondrial function (for improved energy levels) and total testosterone levels.
Red ginseng also has beneficial effects on the prostate gland, and has been found to activate androgen receptors to improve testosterone response.
Can Testogen work for you?
There is a convincing body of evidence to suggest that the ingredients in Testogen can support the healthy production of testosterone hormone, and the way cells respond to its effect. This might improve muscle mass and strength in combination with a body-building program. It may also help to boost energy levels and a flagging sex drive. The only way to tell it if will help you as an individual is to take it for a month to see if you notice any benefit. Please share your experience (anonymously) via the comments below.
Dose: 4 capsules approximately 20 minutes before breakfast.
NB If you have symptoms that suggest testosterone deficiency, do see your doctor as you may need prescribed testosterone replacement.
Medical testosterone treatment
Testosterone replacement is prescribed as tablets, capsules, skin patches, injections (some given two to three times a week, others once every 2 – 3 weeks), implants (replaced every 6 months) or gel. Beneficial effects usually occur within two weeks of starting treatment.
In men with low testosterone levels, taking testosterone replacement therapy will improve sexual function, muscle mass, mood and well-being, with sex drive usually perking up within 4 to 6 weeks of starting treatment.
For those with erectile dysfunction, having a normal testosterone level also increases the chance of a good response to oral drugs such as sildenafil (Viagra), as testosterone is pivotal to the way these work.
In men with low testosterone levels, taking testosterone replacement therapy will improve sexual function, muscle mass, mood and well-being, with sex drive usually perking up within 4 to 6 weeks of starting treatment.
For men with erectile dysfunction, having a normal testosterone level also increases the chance of a good response to oral drugs such as sildenafil (Viagra), as testosterone is pivotal to the way these work.
Testosterone and sex drive
The so-called Testosterone Trials involving 790 men with low testosterone levels compared the effects of testosterone replacement therapy against inactive placebo. Those receiving testosterone were dosed to achieve blood testosterone levels within the normal range for men aged 19 to 40 years. Testosterone treatment was associated with significantly improved sexual desire, sexual activity and erectile function, as well as improvements in mood and depression.
Testosterone and heart disease
Not so long ago, testosterone was blamed for many male problems, including middle-age spread and an increased risk of coronary heart disease. This was due to the fact that men have more heart disease than women, and also produce more testosterone. But this proved to be faulty logic, and it’s now recognised that testosterone itself is not to blame – it’s a lack of testosterone that is the root cause of these problems.
Men with persistently low testosterone levels have a higher mortality rate than those with a normal level. This is because testosterone deficiency is associated with metabolic changes (known as metabolic syndrome) which are associated with high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol balance and poor glucose control. These, in turn, increase your chance of type 2 diabetes, heart attack and stroke.
A study involving 858 veterans, for example, found that men with untreated low testosterone levels were 88% more likely to die over an 8 year follow-up period than those with testosterone levels in the normal range, even after adjusting for chronic illnesses. Although this sounds scary, the good news is that, if your testosterone deficiency s diagnosed and treated, then your health is likely to improve significantly. It will also improve loss of energy, low stamina, fatigue and depression.
This is closely linked with abdominal obesity and with insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, high blood pressure, abnormal blood fat levels (raised triglycerides and LDL-cholesterol) and increased blood stickiness. Put these metabolic risk factors together, and men with low testosterone levels have a significantly increased risk of developing both coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
For men with type 2 diabetes who also have a confirmed testosterone deficiency, prescribed testosterone replacement therapy can help to improve insulin resistance, glucose control, body-mass index, waist circumference and cholesterol levels. Together, these improvements will reduce your risk of heart problems. It can also improve some conditions that may already be present such as angina and heart failure.
Statins lower testosterone in men and women
While the usual cause of a low testosterone level in men is reduced production in the testes (hypogonadism). This can cause cholesterol levels to rise so that your doctor recommends taking a statin drug. It is not widely recognised that taking a statin can lower your testosterone levels even further.
Statins (simvastatin, atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, rosuvastatin and pravastatin) reduce cholesterol production – and cholesterol is the building block you need to make testosterone. The results from 11 clinical trials, involving 501 men show that taking a statin lowered testosterone levels by 0.66 nmol/l (19 ng/dL). Another 6 trials involving 368 women with polycystic ovary syndrome, found that statins lowered testosterone by 0.40 nmol/l (11.5 ng/dL) which in this case is a good thing.
As well as lowering testosterone levels, taking a statin lowers levels of coenzyme Q10 and vitamin D and taking supplements of these may help to reduce statin side effects such as muscle aches, weakness and fatigue.
Testosterone in women
In women, testosterone is mostly concerned with regulating libido, through interactions with DHEA, oestrogen, progesterone and by lowering levels of prolactin hormone. Testosterone levels in women aged 40 years are around half the levels found in those aged 20 years. This decline in testosterone levels may account for low sex drive in some older women, as part of the so-called female androgen deficiency syndrome.
The prescribing of testosterone hormone to women remains controversial. Some menopause doctors specialise in prescribing testosterone supplements to women, alongside oestrogen hormone replacement, to restore energy levels and libido. This has been shown to increase sex drive, and provide greater satisfaction, and pleasure. This must be done carefully to avoid potential side effects such as acne, increased facial hair and an irreversible deepening of the voice. Excessive doses may cause flushing, sweating, vaginal itching and clitoral enlargement.
What is your experience of testosterone supplements or prescribed therapy?







